Your engine burns a very precise ratio of air and fuel. Too much air and it will run hot or “lean.” Too much fuel, and it will choke, running “rich.” The mixture has to be just right. The O2 sensor is responsible for measuring that mixture. If that little sensor goes bad, it can cause all kinds of engine trouble.
What an Oxygen Sensor Does
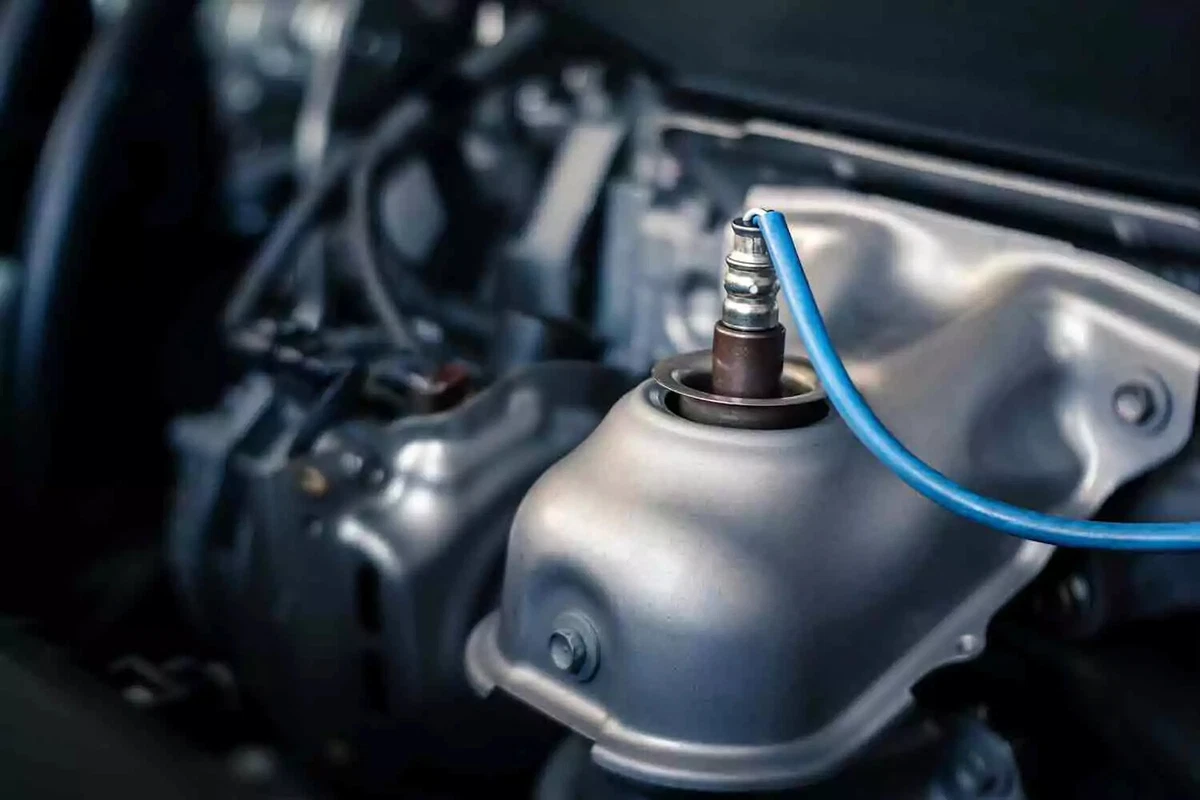

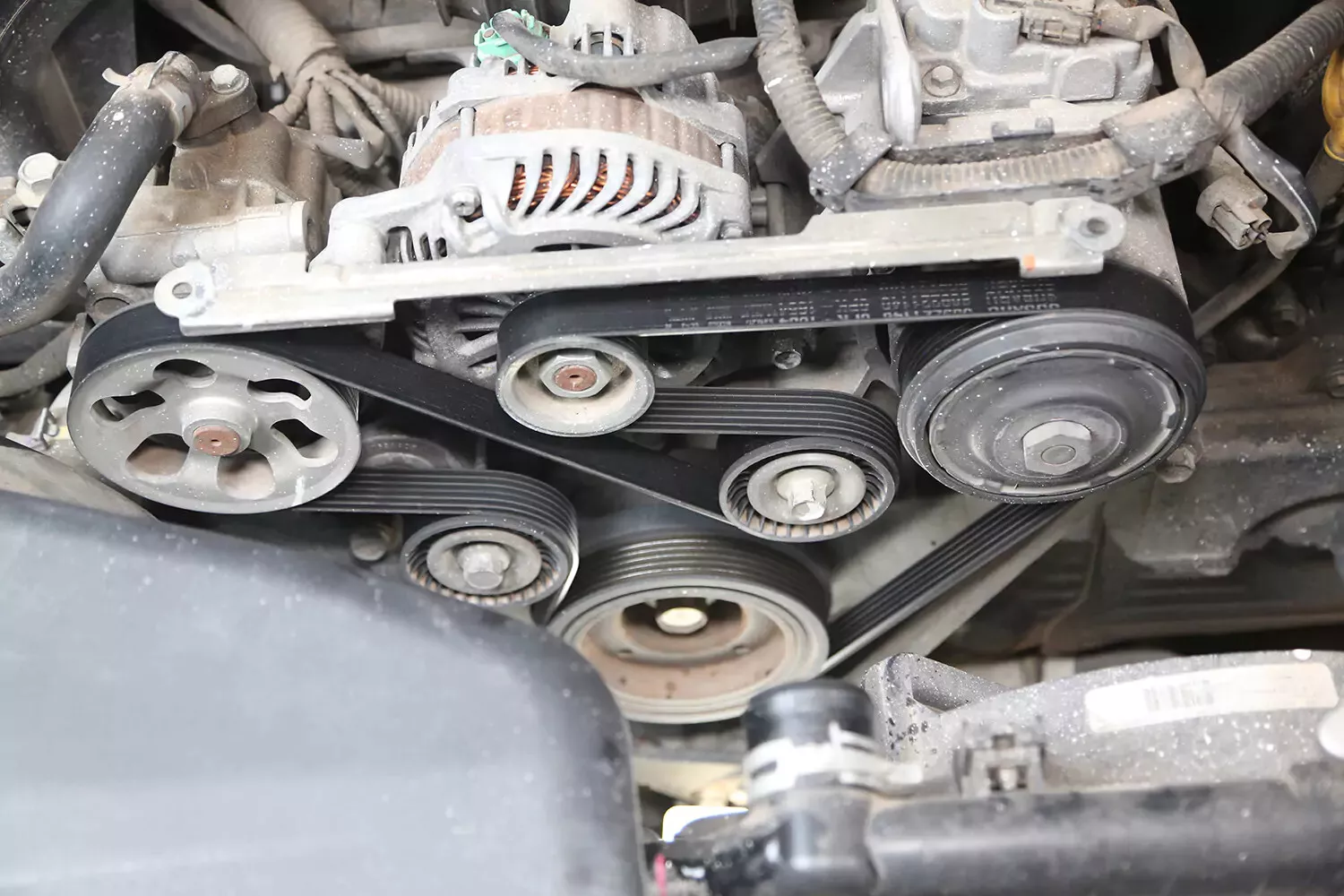
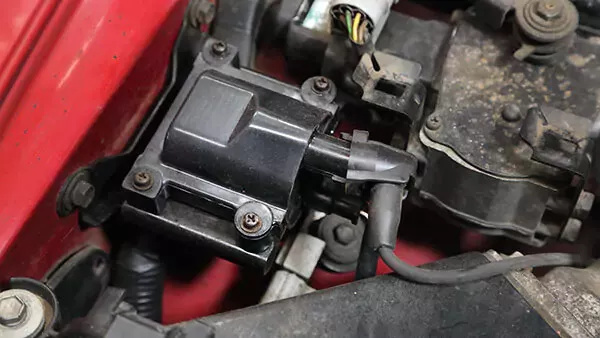
An upstream oxygen sensor mounted in the exhaust manifold of a new vehicle.
Your O2 sensor measures the difference between how much oxygen is in the exhaust and how much oxygen is in the outside air. This difference produces a voltage in the O2 sensor.
The O2 sensor sends that information to your car’s computer—the engine control unit (ECU). It’s this ratio that lets the O2 sensor measure if your engine is burning the right ratio of air and fuel.
That ratio of air and fuel can also be represented as a lambda, which is why, in the 1970s, the first O2 sensors were called lambda sensors. Old Volvos even had a little badge in the shape of the Greek letter lambda to advertise what was then cutting-edge technology.
Your vehicle most likely has two types of O2 sensors: upstream and downstream. The upstream sensor is located before the catalytic converter in the exhaust system and checks the quality of the air-fuel mixture in the engine.
The downstream sensor comes after the catalytic converter and monitors the condition of the converter and its effectiveness in reducing harmful emissions. While the downstream sensor is important, an issue with the upstream sensor is more likely to affect how your vehicle runs.
How Long Oxygen Sensors Should Last
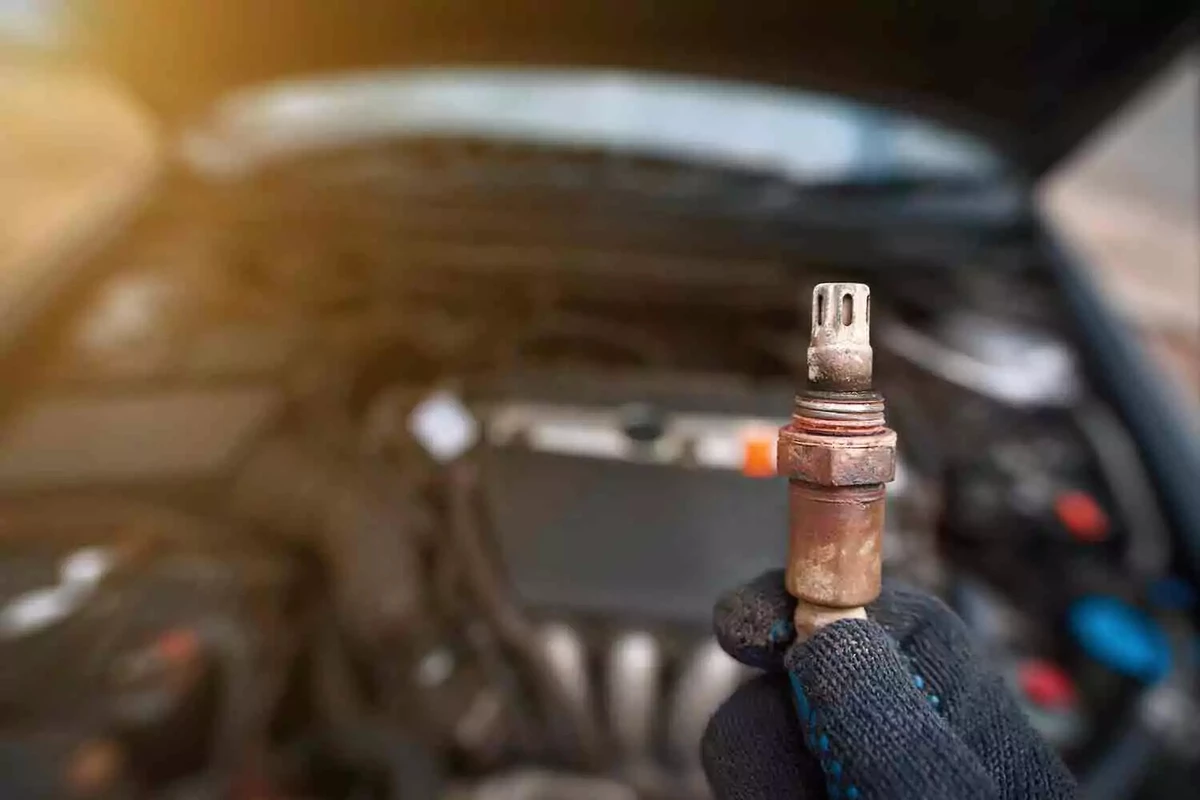

You can replace an oxygen sensor after it fails. A better approach is to replace it as preventive maintenance.
In normal driving conditions, you can count on a sensor to last between 60,000 and 100,000 miles. However, some factors can cut down that lifespan, such as:
Bad gas: Poor fuel quality has a big impact on oxygen sensors and causes carbon buildup, which reduces the sensor’s effectiveness.
Hard driving: If you regularly drive in extreme temperatures, do a lot of stop-and-go driving, or go off-roading, the extra stress on the sensor can cause it to wear out quickly.
Misfires: Engine misfires can push unburned fuel into the exhaust system and deteriorate your oxygen sensor.
Signs of a Bad O2 Sensor
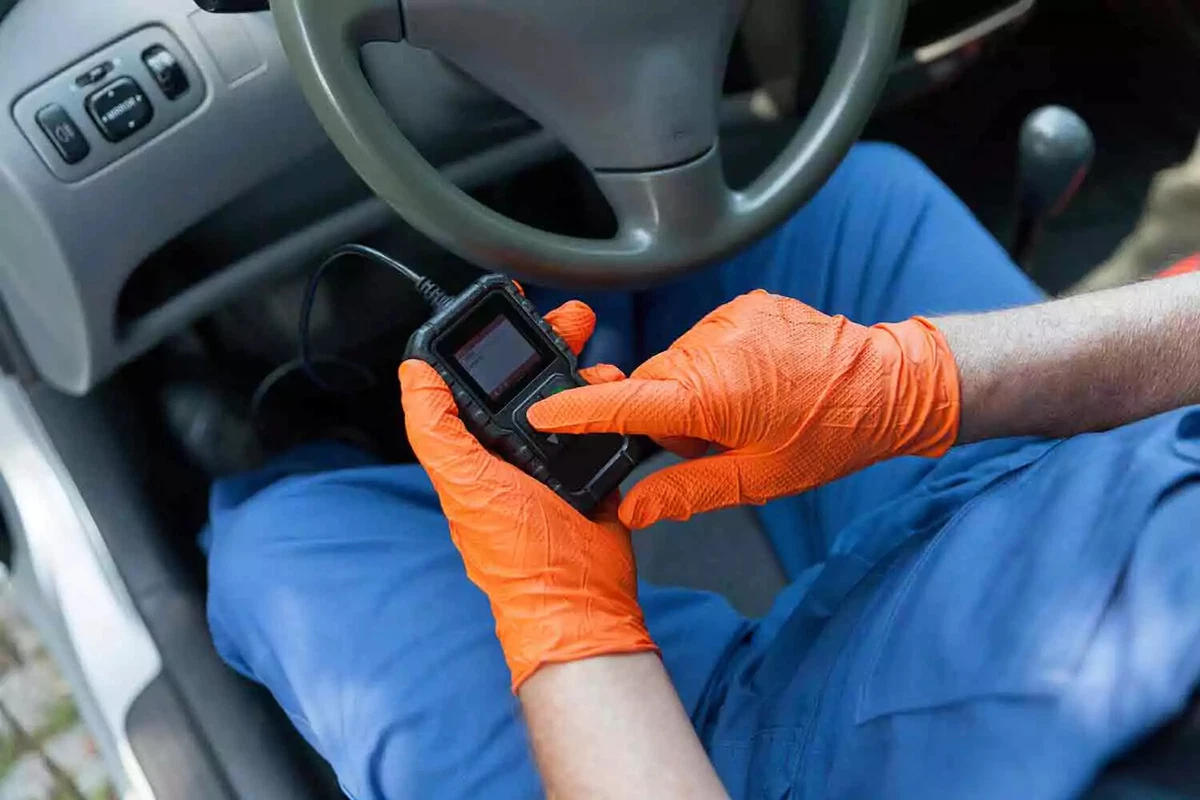

If a check engine light is displayed, an OBDII code reader will decipher the code.
The most common sign of a bad oxygen sensor is a check engine light. When the sensor fails to send a signal to the ECU, this triggers a diagnostic trouble code and turns on the check engine warning. If the check engine light is on, you may fail an emissions test. Any kind of issue with your exhaust and the makeup of its emissions could be a sign that you have a bad or dirty O2 sensor.
Rough idling is another common symptom of a bad O2 sensor. When the sensor goes bad, the ECU can’t properly adjust your air-fuel mixture. It can cause your engine to run hot and lean with not enough fuel. It can also cause your engine to run too rich and use more fuel than it needs. If you notice that you’re making more trips to the gas station than usual and your engine feels rough, these are common signs that the O2 sensor has failed.
If your vehicle is exhibiting any of these symptoms, check the oxygen sensor. However, other areas of the emissions system could also be the culprit. It’s a good idea to check your catalytic converter, air intake, and spark plugs to make sure that they’re not causing the rough idle or diagnostic codes.
While you may be able to drive your car with a bad oxygen sensor, doing so for an extended period can damage the engine and exhaust system. Driving with a bad sensor creates carbon buildup in your exhaust system. It can damage the catalytic converter, which is increasingly expensive to replace. It can also gum up the car’s fuel injectors, which are another costly replacement. Replace a faulty sensor as soon as possible.
Replacing an Oxygen Sensor Isn’t Complicated
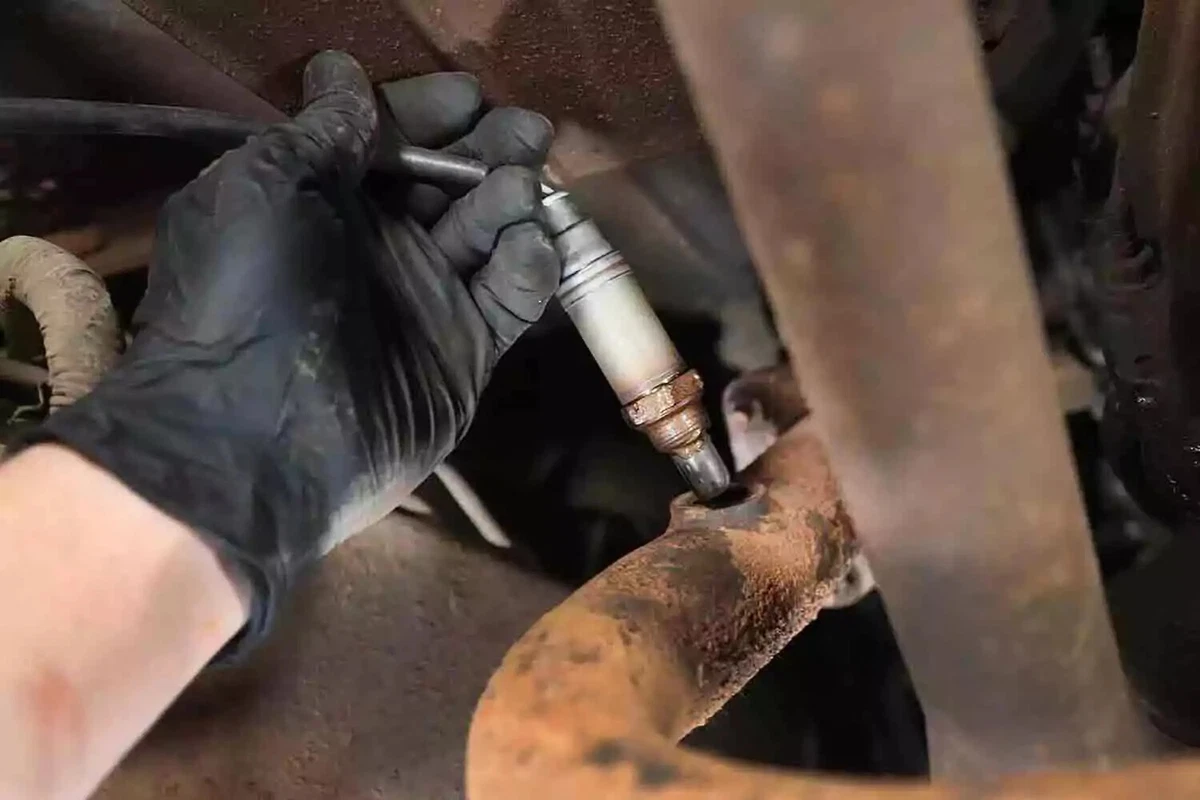

Always use a generous coating of dielectric grease on the oxygen sensor’s threads to prevent it from seizing in the bung over time.
Replacing an O2 sensor is a relatively simple job that should not take more than an hour. Our complete how-to guide and video - opens in new window or tab. has detailed instructions.
In a nutshell, you take out the old O2 sensor and put in a new one. You can use an oxygen sensor socket or an open-end wrench for the job, but with either, be delicate. Disconnect wires gently, apply anti-seize on your new sensor, and be careful not to cross-thread anything going back in.
If you aren’t sure whether the upstream or downstream sensor has failed, it’s best to replace both so you can be sure the exhaust system is in good working order. You can find the location of the sensor by checking your vehicle’s service manual or by looking for the component attached to the exhaust pipe with a connection to the car’s electrical wiring.
How much should you spend on a new O2 sensor?
A standard O2 sensor costs between $20 and $100, depending on if you are getting aftermarket or original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. Use the eBay Parts Finder - opens in new window or tab. to find an O2 sensor that fits your vehicle. Plug in your complete year, make, model, engine, and trim information.
To do the replacement job, you may also need some specialized tools like an oxygen sensor socket and an anti-seize compound. Those can cost between $20 and $100 as well. If you are going to replace both of the sensors yourself, you can expect to spend between $60 and $300 for the right tools and parts to complete the job.
Share your feedback
This article is meant to provide general guidance only. Automotive maintenance, repair, upgrade, and installation may depend on vehicle-specifics such as make and model. Always consult your owner's manual, repair guide for specific information for your particular vehicle and consider a licensed auto-care professional's help as well, particularly for advance repairs.